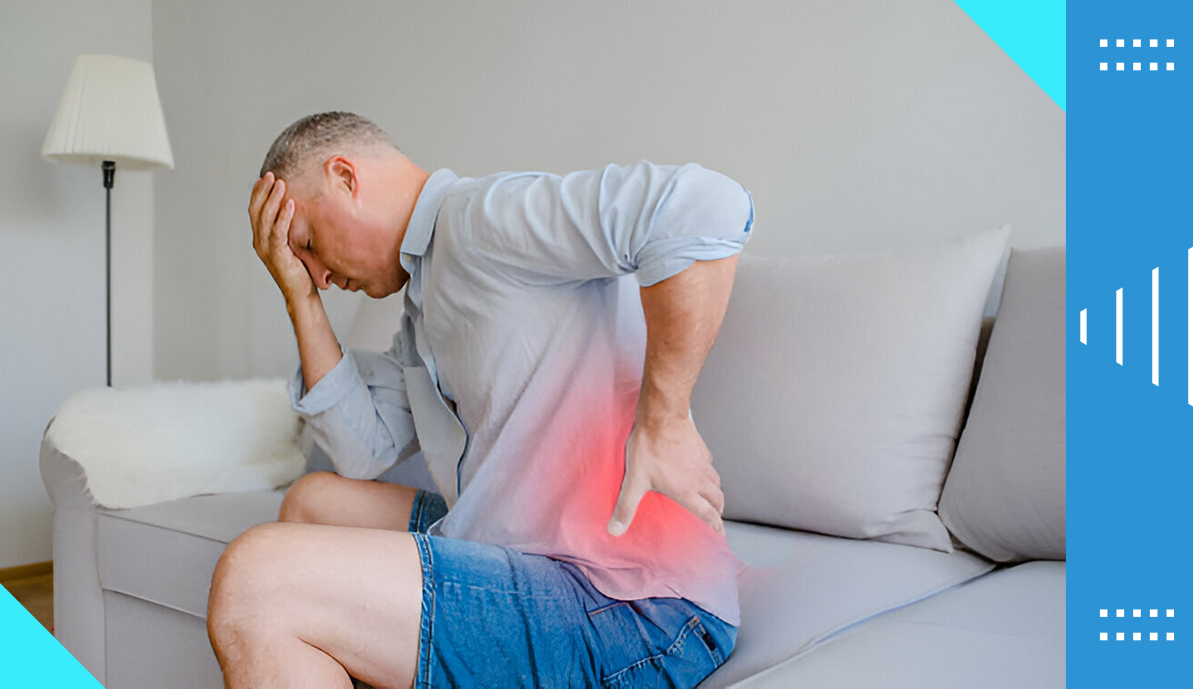
In simple words, analgesics are painkillers. The medicines work by decreasing inflammation or by distracting the brain from the symptoms. From headaches to arthritis to injuries, analgesics can bring a faster recovery from the pain. The medication reduces inflammation caused by injuries and offers relief. Opioid analgesics turn the brain from the pain signals. Some painkillers are available over the counter, whereas some need a prescription. A large number of painkillers from various brands are available on the market. The medicines are available in multiple forms – liquid (oral use), intravenous, suppositories, creams, patches, gels, ointments, etc.
Unlike anesthetic substances, analgesics don’t cause a loss of consciousness in the affected body part. The drugs are also known as pain relievers. Some of the most in-demand painkillers include Carisoprodol 350 mg, Tapentadol Tablets, PREGABALIN CAPSULES, GABAPENTIN TABLETS, Aspadol 50, and more. You can order the medicines online at Global Care Meds and receive premium-quality drugs with fast shipping across the USA. The blog discusses what analgesics are, what their uses are, what types of analgesics are available, and how the medicines work.
How Do Analgesics Work?
Different types of analgesics work in different ways. The medicines relieve pain and inflammation. Doctors prescribe pain killers to reduce pain after surgeries and injuries. The medicines relieve acute and chronic pain, such as pain killers for back pain. Muscle cramps and menstrual pain also come under control with the aid of analgesics.
There are two major groups of analgesics: opioids and anti-inflammatory analgesics. Anti-inflammatory medicines work by reducing inflammation at the pain point. Examples include NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Opioids, on the other hand, change the brain’s perception of pain. An opioid can be a natural supplement, a medicine, or a home remedy.
What Are the Types of Analgesics?
A large number of analgesics are available, but there are two main types.
- NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs)
NSAIDs include diclofenac, ibuprofen, and naproxen. Medical professionals prescribe the drugs in low doses to resist blood clots, especially for those with health issues. The drugs block the chemical effect called cyclo-oxygenase enzymes. When a person is injured, prostaglandin makes the person feel the intensity of the pain, causing inflammation in the area. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin secretion, reducing pain and inflammation.
- Weak Opioids and Strong Opioids
Opioids work by aligning opioid receptors in the Central Nervous System. Weak opioids like codeine and dihydrocodeine are highly effective in treating severe pain. The medicines can turn into addiction and bring adverse effects on the body. Strong opioids include morphine, pethidine, oxycodone, tramadol, buprenorphine, etc. The medicinal properties boost tolerance to pain. Opioids reduce the transmission of pain impulses. Your doctor can prescribe pain killers after surgery to reduce the intensity of the pain.
Paracetamol is another significant type of painkiller. Paracetamol is believed to treat pain and bring down body temperature but does not treat inflammation. In need, different painkillers are combined to make a high-dose medicine. Medical professionals also prescribe antidepressant and antiepileptic drugs to reduce neuropathic pain.
How to Take Analgesics?
You should take prescription analgesics based on your doctor’s prescription. Analgesics are available in many forms, which include:
- Capsules and tablets,
- Drops or syrups
- Injections
- Rectal suppositories
- Topical creams, patches, or gel
- Flims to place under the tongue to dissolve
- Nasal Spray
- Powder to mix and take
If you are unsure how to take your analgesic medication, talk to your healthcare professional or pharmacist. A healthcare professional can advise you on the medication dose, course duration, and frequency.
Risks of Use
Non-opioid analgesics for short-term use can pose minimal risks when the person takes the medicines following the proper instructions. Some may suffer side effects, especially when the medication exceeds doses and course duration.
Recipients rarely get addicted to the medicines, but one may get dependent on opioids. Dependence means when the body gets accustomed to the medicine, and now it’s less effective. Then, recipients need high doses to experience the impact of pain relief. Opioids can create addiction and substance use disorder. People suffering from chronic back pain can benefit from pain killers for back pain, but the chances of addiction remain high in such cases.
A few signs of substance use disorder are:
- Intake in larger quantities than the doctor’s prescription
- Intake of the medicine when it’s dangerous, such as driving
- Inability to stop the medicine
- Withdrawal symptoms when the course is at its end
What Side Effects to Consider
The side effects of the medicine intake can range from mild to severe. The lesser serious side effects include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Indigestion
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Heartburn
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- Dizziness
More serious side effects are:
- Skin rash
- Chest pain
- Stomach ulcers
- Sensitivity to light
- Liver damage
- Respiratory trouble
Compared to NSAIDs, non-opioid analgesics also pose a range of side effects, which include:
- Additional pain
- Itching
- Lack of concentration
- Reduced immunity
- Issues with urination and passing stools
- Lack of sex drive
- Reduced fertility
- Erectile dysfunction
- Breathing trouble
You should immediately inform your doctor once you see any of the side effects affecting you after taking the medicine. It’s advisable to refrain from alcohol and smoke consumption as the substances can interact.
Who Can’t Take Analgesics?
Though rarely, one cannot take a painkiller; it needs a doctor’s consultation only when the medicine poses serious side effects like severe allergic reactions. Younger children, pregnant and breastfeeding women, and patients suffering from other diseases must seek a doctor’s advice before taking the medicine. Those who have undergone operations need solid medical advice on pain killers after surgery to reduce the pain. Your doctor will guide you on whether the medicine is safe for you. In your journey to pain relief, Global Care Meds is with you.
Bottomline
Analgesics relieve pain. The medicines treat you by reducing inflammation or changing the perception of your brain. Different types of analgesics are available that your doctor can prescribe you. With Global Care Meds, buy premium quality, selective analgesics namely Flupirtine 100 mg Capsules, Nervisign 300 mg Capsules, Prosoma 350 mg Tablets, Somaboost 750 mg Tablets, Tapdol 100 mg Tablets, Royal 225 mg Tablets